NTU provided technical assistance to the African Union Commission Department of Infrastructure and Energy (AUC-DIE) under the EDF-funded project “Support to the African Union Commission Department of Infrastructure and Energy in transport policy harmonisation and transport sector services development & Support to PIDA PAP for the start-up of smart corridor activities”. This initiative is part of the larger intervention, “Support to the Transport Sector Development Programme” and was supported by a EUR 2.3 million budget. The project's overall objective was to contribute to the achievement of inclusive political, economic, and social development through enhanced regional integration of the Sub-Saharan countries part of the Organisation of African, Caribbean and Pacific States (OACPS).
The programme's specific objective was to enhance Africa's capacity to regulate, organise, promote, and finance improved inter-regional and continental transport infrastructure and services. This was achieved by fostering safe transboundary transport corridors and harmonised transport policies to strengthen interconnectivity across regions.
The work of NTU focused, among others, on facilitating the implementation of PIDA-PAP (Programme for Infrastructure Development in Africa - Priority Action Plan) projects.

NTU provided technical assistance to the African Union Commission Department of Infrastructure and Energy (AUC-DIE) under the EDF-funded project “Support to the African Union Commission Department of Infrastructure and Energy in transport policy harmonisation and transport sector services development & Support to PIDA PAP for the start-up of smart corridor activities”. This initiative is part of the larger intervention, “Support to the Transport Sector Development Programme” and was supported by a EUR 2.3 million budget. The project's overall objective was to contribute to the achievement of inclusive political, economic, and social development through enhanced regional integration of the Sub-Saharan countries part of the Organisation of African, Caribbean and Pacific States (OACPS).
The programme's specific objective was to enhance Africa's capacity to regulate, organise, promote, and finance improved inter-regional and continental transport infrastructure and services. This was achieved by fostering safe transboundary transport corridors and harmonised transport policies to strengthen interconnectivity across regions.
The work of NTU focused, among others, on facilitating the implementation of PIDA-PAP (Programme for Infrastructure Development in Africa - Priority Action Plan) projects.
Implementation
NTU supported PIDA PAP with the launch of smart corridor activities. The first step was to select two pilot projects. Consequently, NTU undertook the following actions:
-
Smart Corridor Definition and Characteristics,
-
Multi-factor criteria for selecting the pilot smart corridors.
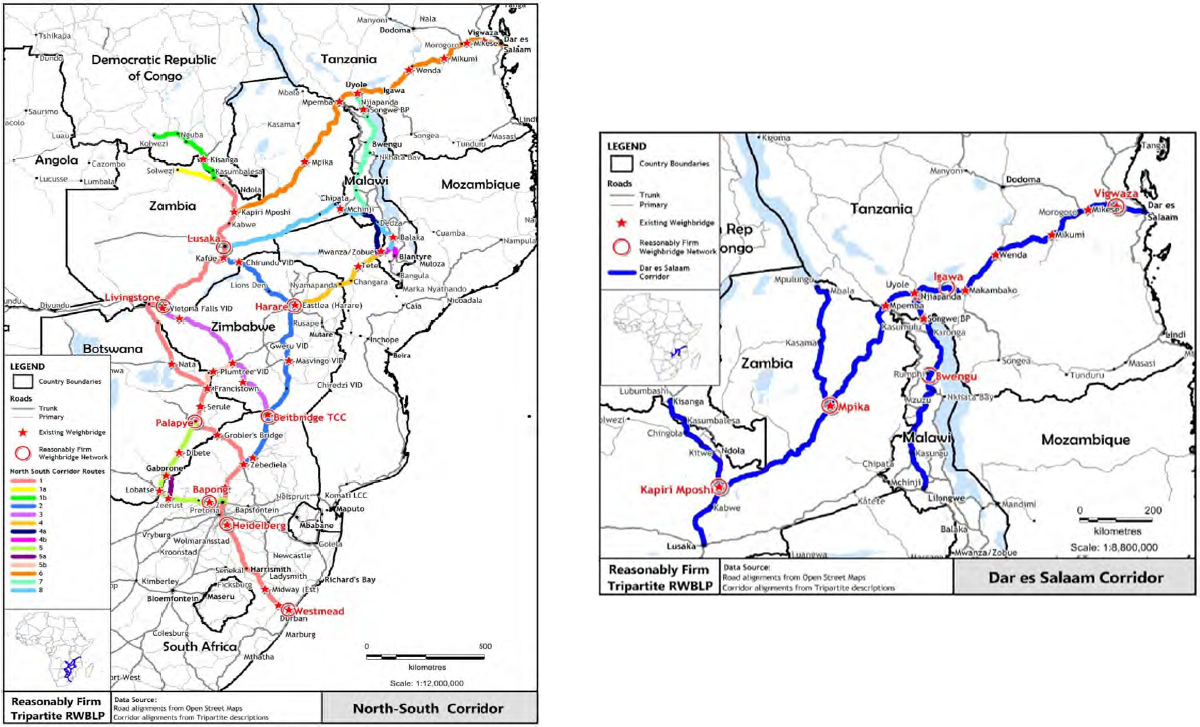
An assessment of transport corridors was conducted based on these actions, resulting in a ranking of the top ten potential corridors. The Validation Committee reviewed and approved the recommendation to select the North-South Corridor (NSC) and the Dar es Salaam Corridor (DC) as pilot projects.
NTU's team undertook desk research and two field visits to both corridors. The purpose was to obtain information to carry out a gap analysis between the current status and the planned activities concerning the following aspects:
-
Corridor Coordination and Management
-
Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS)/Information Communication Technology (ICT)
-
WTO Trade Facilitation Measures
-
Regional Economic Communities Trade Facilitation Measures
-
Infrastructure Provision and Maintenance
The field visits were critical for obtaining information necessary for the project team to undertake the following activities for the design and costing of the two corridors:
-
Gap Analysis of the existing corridors versus what should be done for the corridors to convert them into Pilot Smart Corridors;
-
Identification of activities that must be undertaken to close the gaps;
-
Costing of the activities required to convert the NSC and DC into Pilot Smart Corridors;
-
Draft Report for the PSCs Stakeholder Workshop to agree on the activities, options and approach;
-
Preparation of TORs for facilitating and coordinating the implementation of the activities;
-
Development of a report on the Design and Costing of NSC and DC PSCs.
As a result, several activities aimed at addressing the identified gaps have been defined, cost, and prepared for inclusion in the future implementation of the Pilot Smart Corridor programme. Moreover, a Transport Policy Paper was drafted, recommending a number of general and specific policy measures to improve the overall efficiency of the transport sector in Africa. This document includes Policy Guidelines, which help local decision-makers in translating policies into actions.

Impact
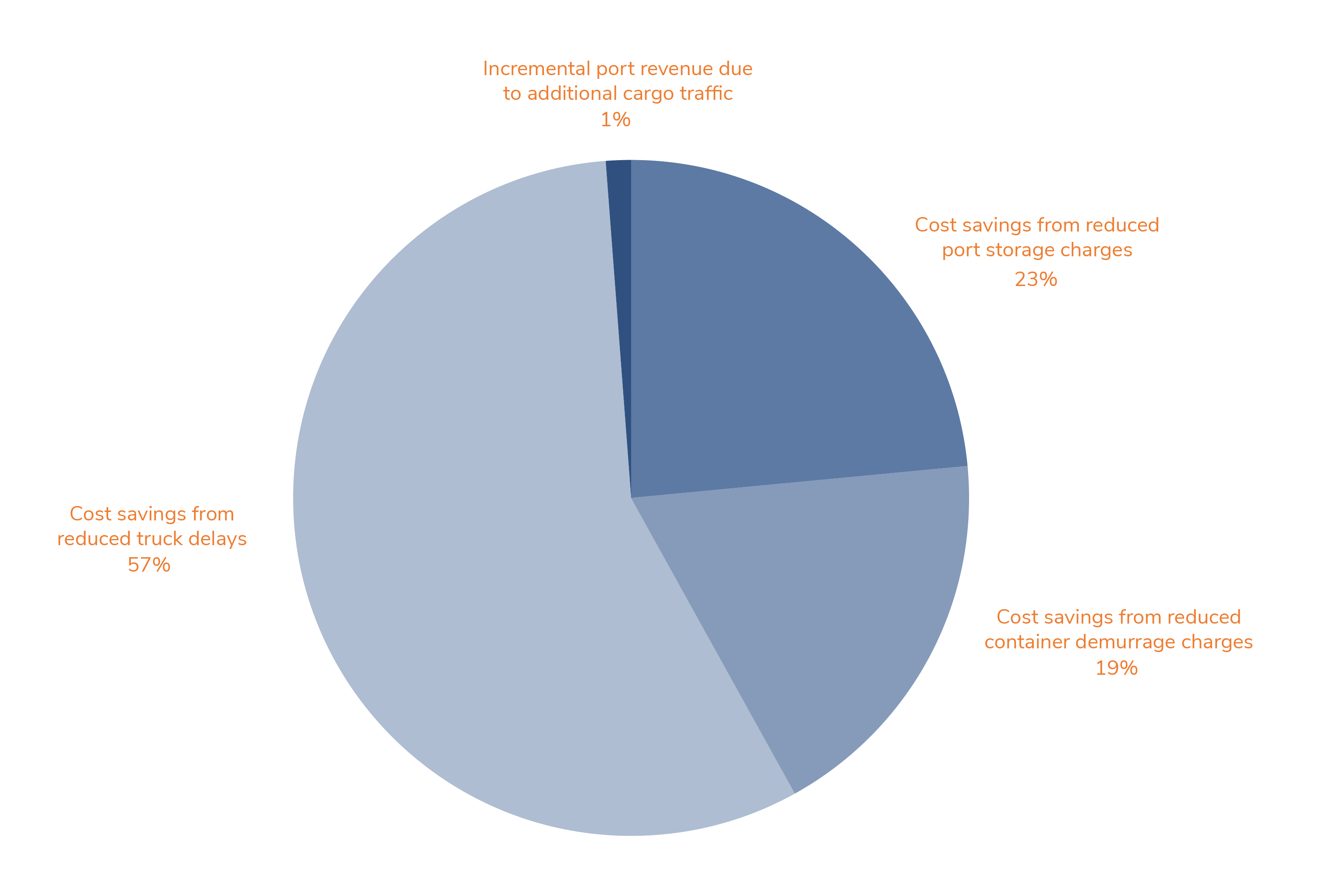
The activities carried out by NTU provided valuable insights into improving the quality of transport infrastructure—including ports, roads, border crossings, and railways—within the North-South Corridor (NSC) and the Dar es Salaam Corridor (DC), facilitating their transformation into Pilot Smart Corridors. When executed, these measures will improve the corridors' efficiency, reduce the cost of transport, and foster trade.
In addition, the Report on the Design and Costing of NSC and DC Pilot Smart Corridors brought clarity to the next steps towards improving regional integration in Africa and capturing the most urgent areas of action.
SDGs




