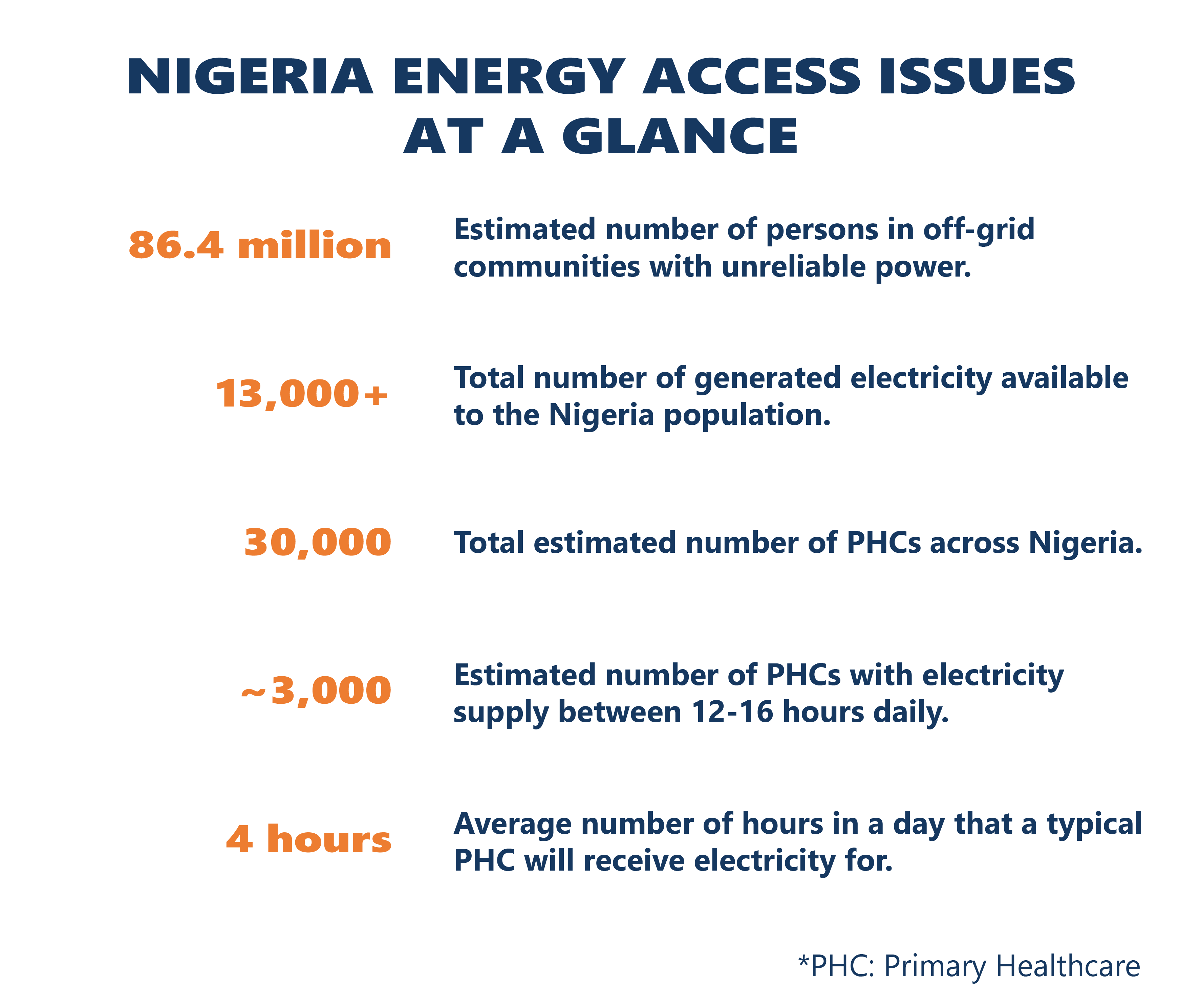
Nigeria faces significant energy challenges, with many rural areas lacking reliable electricity despite investments in the national grid. The EU-funded Nigeria Solar for Health Project (NISHP) exemplifies the transformative potential of renewable energy in addressing these gaps. By equipping underserved healthcare facilities with reliable solar power systems, including standalone solar home systems (SHS) and mini-grids, the project ensures continuous electricity supply, enhancing healthcare delivery, especially during emergencies. NISHP aligns with Nigeria’s decarbonisation goals under the Energy Transition Plan, reducing reliance on diesel generators and promoting environmental sustainability. The project also strengthens local capacity by engaging community stakeholders in system operation and maintenance.
As a scalable model, the project demonstrates how off-grid solar solutions can complement national energy strategies, delivering critical social and economic benefits to remote areas while mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. This initiative represents a significant step towards achieving sustainable energy access and improved healthcare outcomes in Nigeria.

Implementation
NTU approach to the Nigeria Solar for Health Project implementation is built on 6 core pillars, covering the entire project lifecycle. These pillars ensure the sustainable deployment of solar microgrids in healthcare facilities, enhancing healthcare delivery and community empowerment. We integrate technical precision, capacity building, and social impact assessment to achieve lasting benefits, aligning with stakeholder and donor expectations. Advanced project management tools are used to streamline stakeholder engagement, site selection, and system design, ensuring efficiency at every phase.
Our technical expertise enables precise solar microgrid design and installation, incorporating energy audits and load assessments. Data-driven impact assessment methods, such as baseline studies and post-implementation evaluations, are applied to measure outcomes and improve performance. At the same time, capacity building through workshops and training successfully empowers stakeholders with operational and maintenance skills. Through innovative communication and adherence to the EU visibility standards, we ensure extensive outreach, showcasing the socio-economic and environmental benefits of the project.
Impact
-
Improved Healthcare Delivery: The project provides reliable solar power to healthcare facilities, enhancing service quality and ensuring uninterrupted power for critical medical needs.
-
Energy Access: It addresses Nigeria’s energy challenges, expanding access to clean, reliable energy in healthcare facilities and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
-
Environmental Impact: The project supports environmental sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and aiding Nigeria's Paris Agreement commitments.
-
Economic and Social Empowerment: By providing energy to local communities and productive users, it stimulates economic growth and improves livelihoods.
-
Capacity Building: Training and workshops empower local stakeholders to maintain solar systems, ensuring the long-term sustainability of installations.
-
Policy Alignment and Long-term Impact: The project aligns with national policies, strengthening healthcare infrastructure and informing future energy policies.
SDGs:
This project contributes to achieving the following Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):





